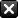No annual account fees or minimums
There's no minimum to open and no account fees to open a Fidelity-managed 529 account.
Tax-smart savings
Any earnings grow federal income tax–deferred, plus get tax-free withdrawals for qualified education expenses.
Flexible use of funds
Pay for college, trade school, and K–12 nationwide, including tuition, fees, and books.1
Where do you live?


The AZ529 plan may be a great option for Arizona residents. Not from Arizona? Be sure to consider your own state plan as it may have additional benefits, including state tax advantages.


The CHET 529 Plan may be a great option for Connecticut residents. Be sure to consider your own state plan as it may have additional benefits, including state tax advantages.


The DE 529 Plan may be a great option for Delaware residents. Be sure to consider your own state plan as it may have additional benefits, including state tax advantages.


The MEFA U.Fund College Investing Plan may be a great option for Massachusetts residents. Be sure to consider your own state plan as it may have additional benefits, including state tax advantages.


The UNIQUE College Investing Plan may be a great option for New Hampshire residents. Be sure to consider your own state plan as it may have additional benefits, including state tax advantages.


If Fidelity does not manage a 529 plan for your state, the UNIQUE College Investing Plan, our national 529 plan, may be a good option for you. The UNIQUE College Investing Plan is sponsored by the State of New Hampshire and is available to U.S. residents. Before investing, you should consider whether your or the beneficiary's home state offers its residents a 529 plan with alternate state tax advantages or other state benefits such as financial aid, scholarship funds, and protection from creditors.
Saving a little over time can go a long way*
Help reduce the amount of loans borrowed for education expenses
Hypothetical chart
All Fidelity-managed 529 plans earned a best-in-class rating from Morningstar.2
Learn

Explore the latest ways to save and pay for a child’s education with a 529 Plan
Learn how a 529 can help you reach your educational savings goals at any stage of your journey.

The tax-smart way to help save for college
The money moves to help you reach your education goals.

Ways to help maximize your education savings strategies
Planning to help pay for your child’s higher education? Learn how a 529 savings plan can help you get there.

The ABCs of 529 savings plans
Learn ways to explore investment options and potential tax advantages.
Common questions on 529 college savings plans

What is a 529 savings plan?
529 savings plans are flexible, tax-advantaged accounts designed specifically for education savings.
Any earnings on contributions grow federal income tax-deferred, and withdrawals taken to pay for qualified education expenses such as tuition, fees, books, computer expenses, or room and board are free from federal income taxes.

Am I on track? How do I estimate higher education costs?
Anyone can use our college savings calculator to figure out how much to save each month. Login or become a member to create a personalized savings plan and track your progress.
It's hard to predict your child's future educational path. Visit the Fidelity Learning Center for a variety of strategies and tips to help you prepare.

What can I do with the money left in the account?
The 529 account beneficiary can be changed to an eligible family member to use for their qualified education expenses.
Under certain conditions you may be eligible to transfer assets from your 529 to a Roth IRA established for the beneficiary of the 529 account.3
You can also take a non-qualified withdrawal. Only the portion of the non-qualified withdrawal attributed to investment earnings will be subject to federal and state income taxes plus a 10% federal penalty.

How can the gifting feature help out?
Family and friends can contribute easily with our free online gifting feature. Even small amounts can add up over time.
It's as simple as sharing a link to your College Gifting page. And we do not display your account information, helping to protect your privacy.